In the last article I described “how to automatically execute a command on EC2 machine in the AWS cloud”. Now I decided to describe a similar topic. Below I present 3 examples describing how to automatically start EC2 in the AWS cloud.
More and more people are asking me for simple automation examples, so here you go 🙂
Below you will find 3 examples of how to automatically start an EC2 machine in the AWS cloud. The topic seems simple but can be solved in many ways. As they say, many roads lead to the same goal. I will use session manager, CLi and Lambda for this. Everyone can have their own way, use what they like / know more. It is important that the result is correct and that it does not cost too much 😉
Based on these simple examples, you can automate other things. It is worth getting acquainted with them and starting the adventure with automation, because it makes life much easier 🙂
1) Session manager
Sesion manager – permissions
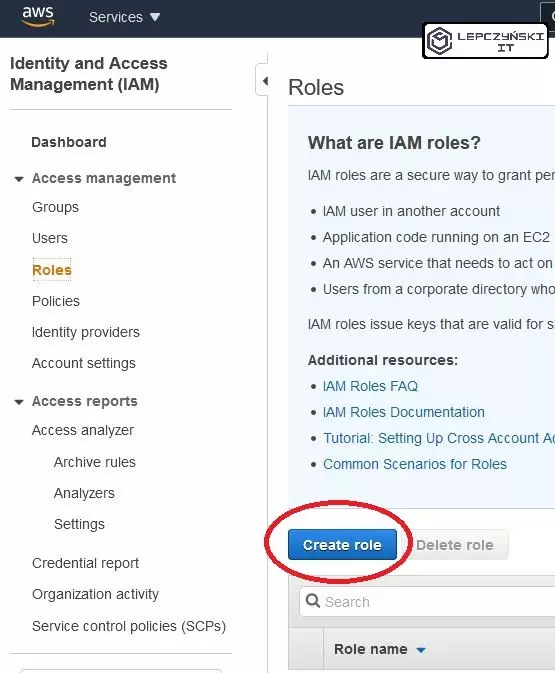
First, you need to create a role that will stop and start EC2 instances. Remember !! Select System Manager as the service that can use the role.
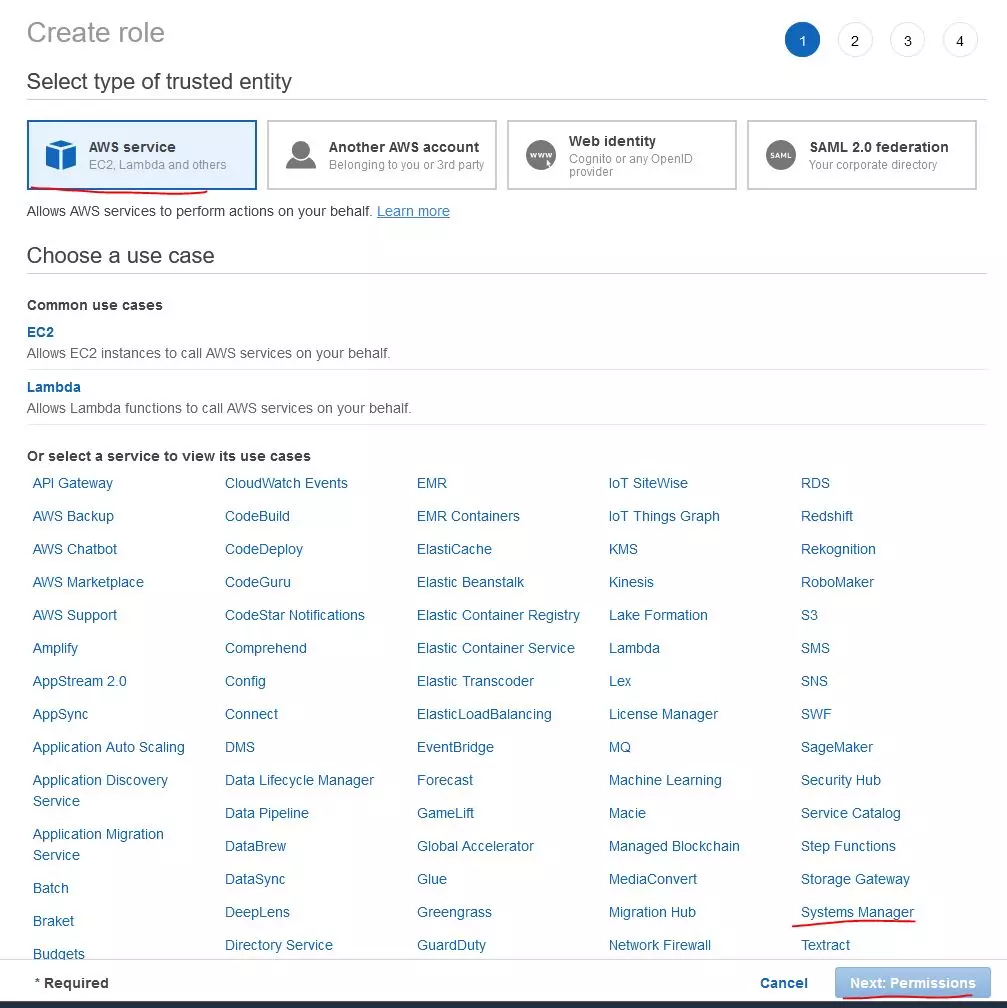
You need to add a policy to the role that allows this to happen. I don’t want to give full permissions to EC2, so I will create a new policy with minimal permissions. The policy will only allow the EC2 machine to be started, stopped and restarted.
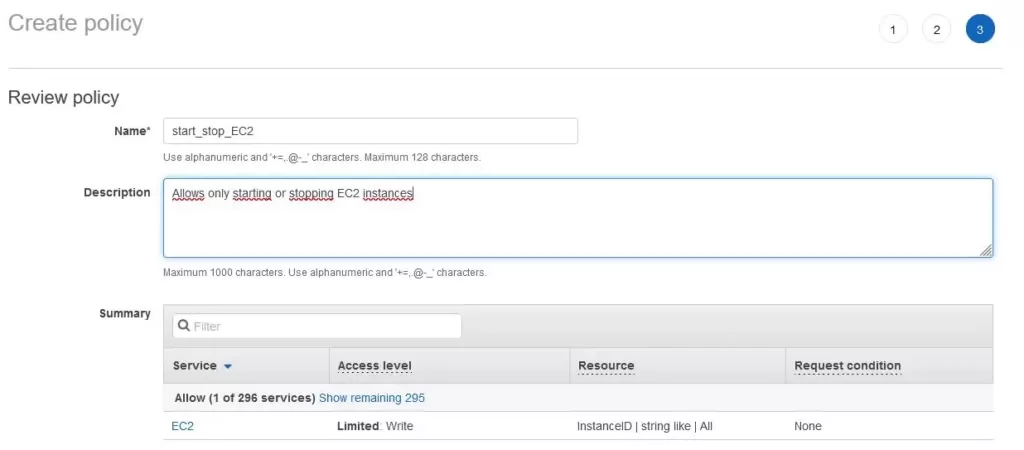
I click on create policy and add the JSON created below. Then I give tags. On the last tab, I provide the name and description for the newly created policy.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:StartInstances",
"ec2:StopInstances",
"ec2:RebootInstances"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ec2:*:*:instance/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ec2:Describe*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Now refresh the list of policies and find the one you just added.
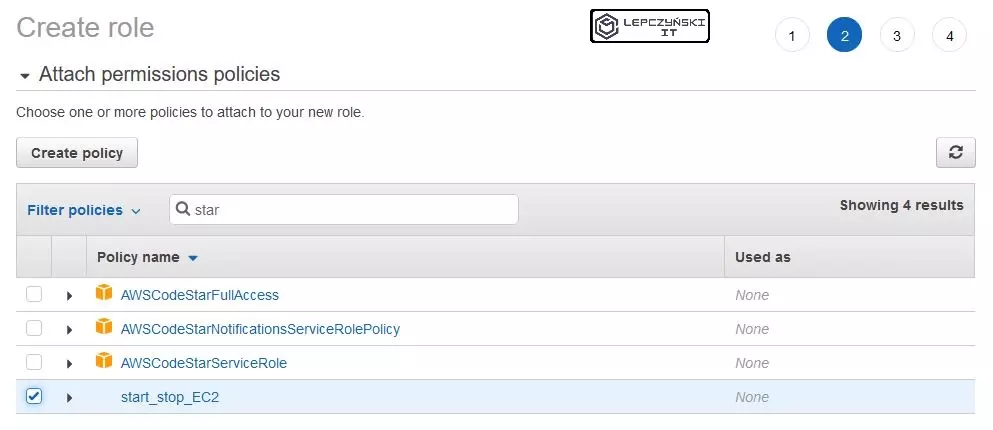
You can go ahead and add Tags. Finally, give it a name and encourage you to create a short description. It’s good to get into this habit of describing everything. It makes work much easier later on. If you work in the cloud a lot, after a few months you will forget why you created this role.
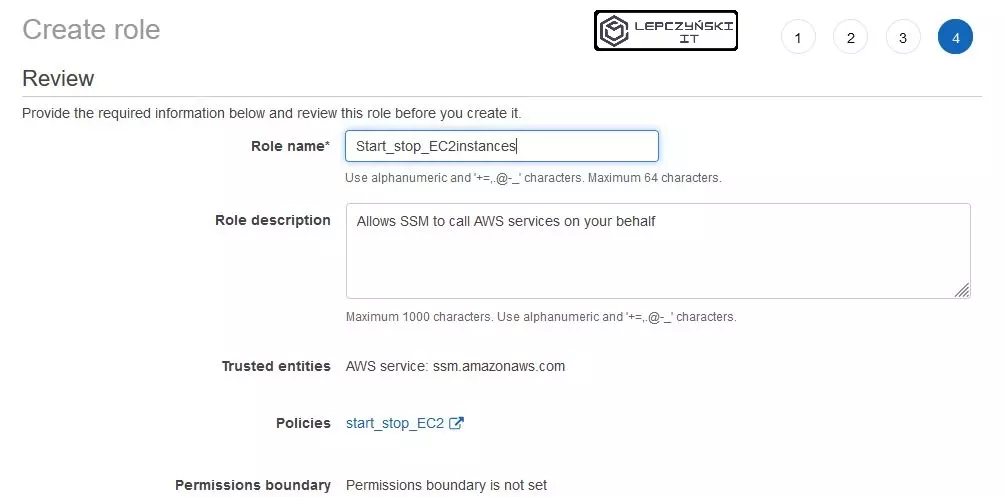
Session manager – commissioning planning
When the role is ready, go to AWS Systems Manager and select State Manager from the left menu.
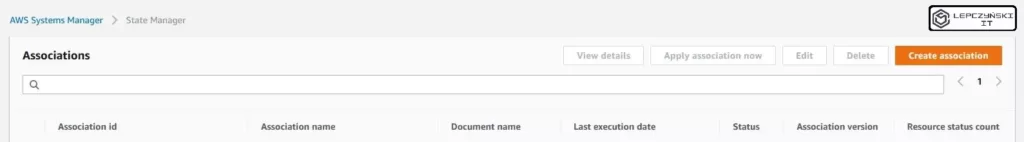
Click Create association, it’s a good idea to enter a name, although it’s not required.
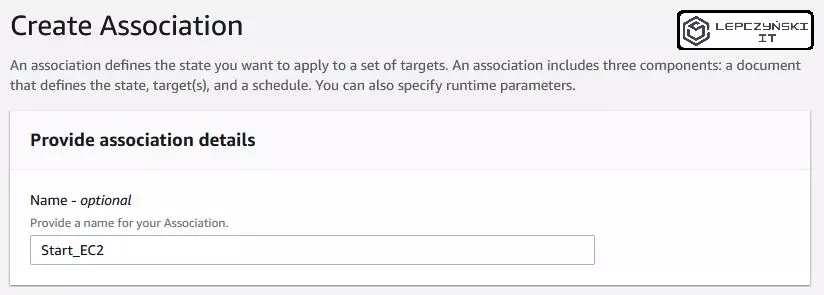
In the next section, select the document named AWS-StartEC2Instance. For simplicity, you can choose simple execution. If you check “Show interactive instance picker” you will get the EC2 list, just select the machines you are interested in from the list and select them.
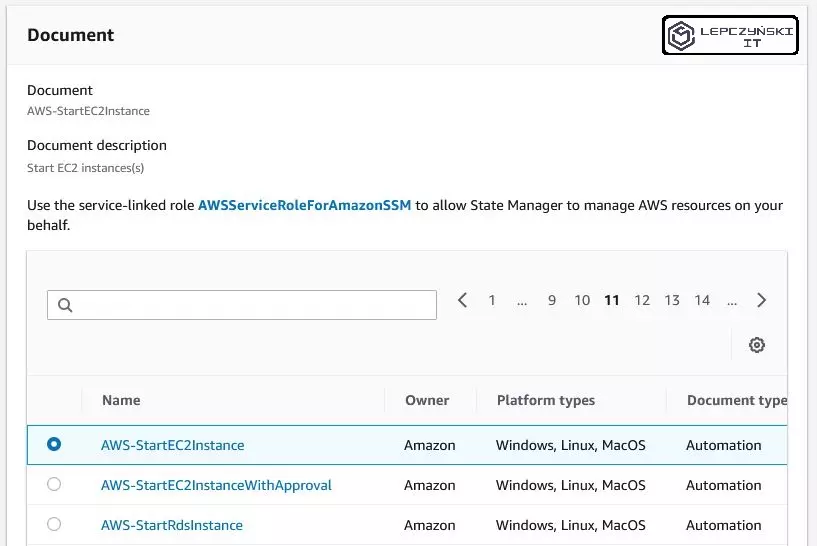
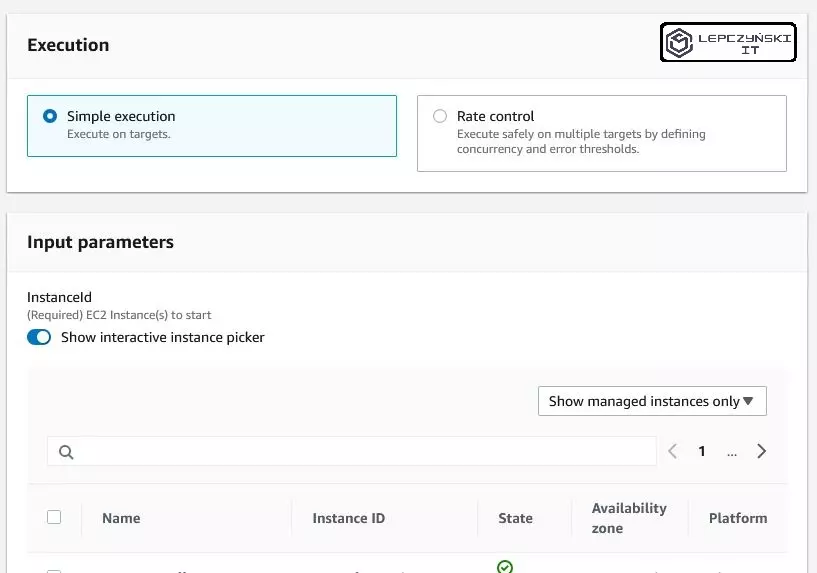
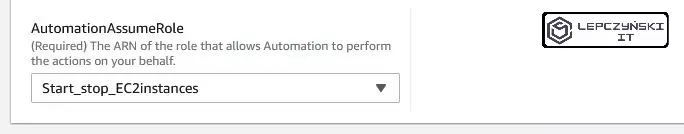
Remember !! As you select the instances, you have the “AutomationAssumeRole” drop-down list below. Select the role you created earlier on it.
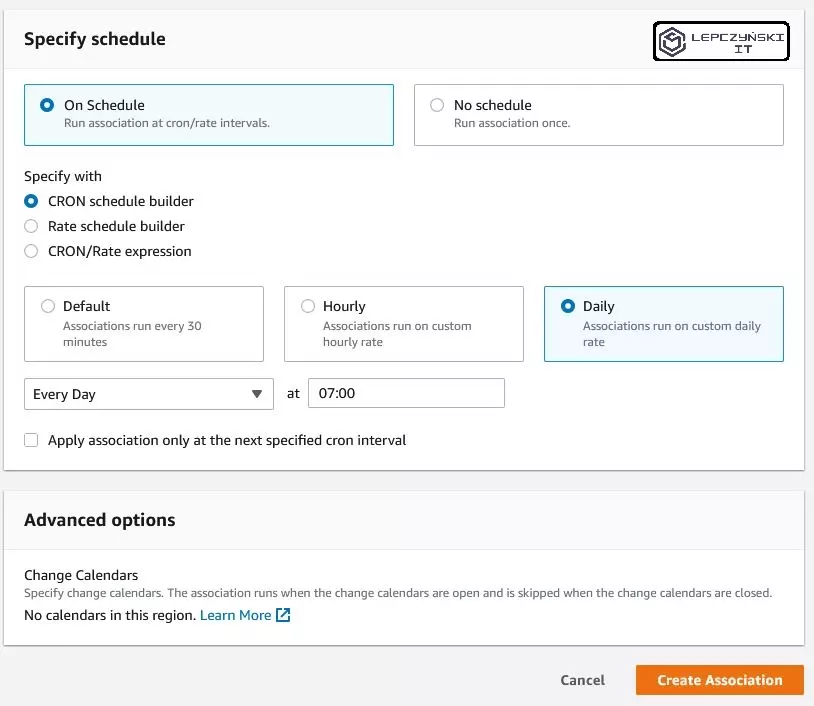
Finally, in the “Specify schedule” section, decide when you want to automatically start the EC2 instance and click “Create Association”.
2) CLI command
On any server, you can run a command that will allow you to run another machine. The EC2 machine should have the permissions to run other machines, it is best to add the needed role for it.
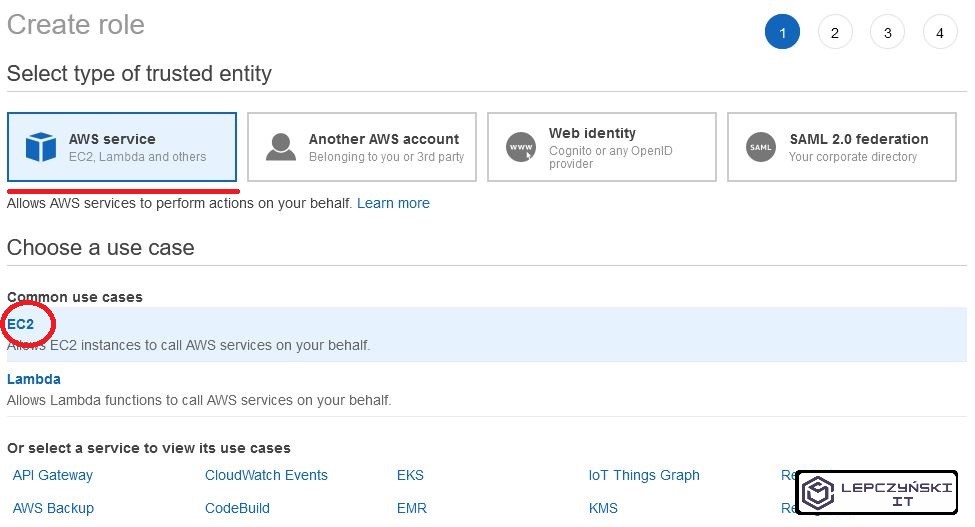
You create a role in the same way as for the first time, only now select EC2 as a trusted entity. Configure the rest the same.
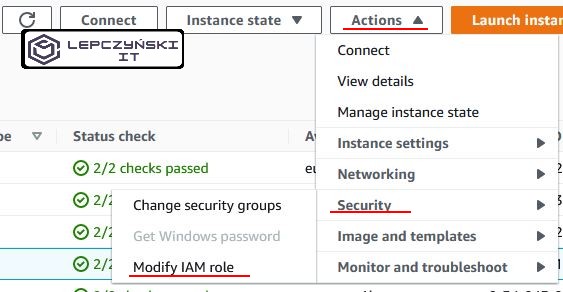
When the role is ready, you can assign it to the EC2 machine, on which you will issue commands to start other machines.
Now log on to the EC2 Machine and check if you have up-to-date aws cli. Execute the command below to check the version.
aws --versionIf you don’t already have aws cli installed, please follow the cli installation documentation.
I always test commands before adding them to cron. I recommend the same to you. Run the command below and check that the EC2 instance of your choice has started. Of course, instead of “YOUR_INSTANCE_ID”, enter the ID of the machine you want to run.
aws ec2 start-instances --instance-ids YOUR_INSTANCE_IDIf everything works fine, run the crontab and add a command to auto-start the selected EC2.
crontab -eThe following entry is an example. It will run from Monday to Friday at 7:00 am. Of course, instead of “YOUR_INSTANCE_ID” enter the ID of the instance you want to run.
0 7 * * 1-5 /usr/local/bin/aws ec2 start-instances --instance-ids YOUR_INSTANCE_IDA good solution is to run a script in the crontab. It may contain commands to start several EC2 machines. The script can be easily edited and managed externally without logging into the machine.
3) AWS Lambda
Lambda – Role
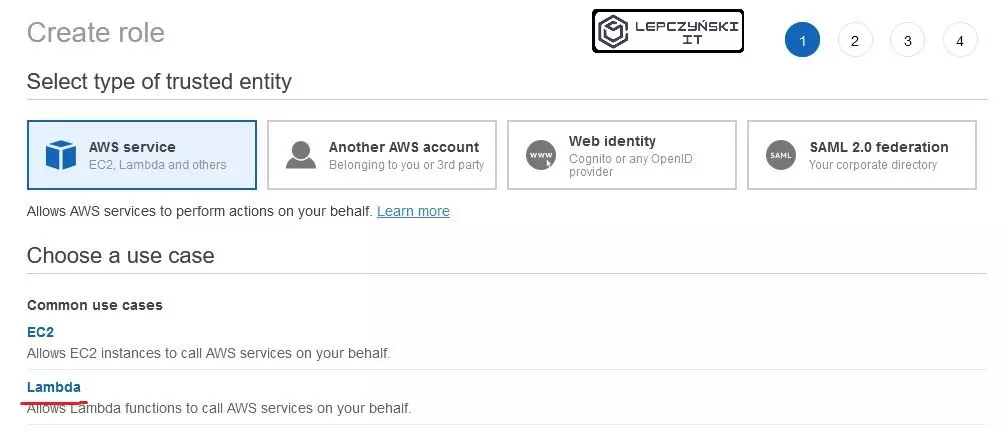
You create a role in the same way as for the first time, only now at the beginning select Lambda as the “trusted entity”. The rest of the configuration is the same.
Lambda – function
Now you can move on to creating a new Lambda function. Open the Lambda service and click “Create function”.
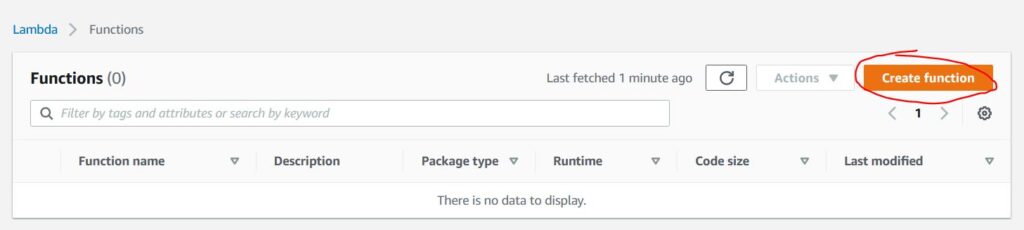
Now select “Author from scratch”. Provide the name of the function and select the language in which you want to write the functions. In my case it is Python 3.8. Below in the Execution role, select an existing role that you previously created for Lambda. You don’t need to add any advanced settings, you can click Create function right away.
Edit the lambda_function.py file so that it has the following content. Of course, replace YOUR_INSTANCE_ID with the ID of the instance you want to automatically run. If you want to run more instances, give their ID after a comma (Remember that the ID should be in ‘ ‘).
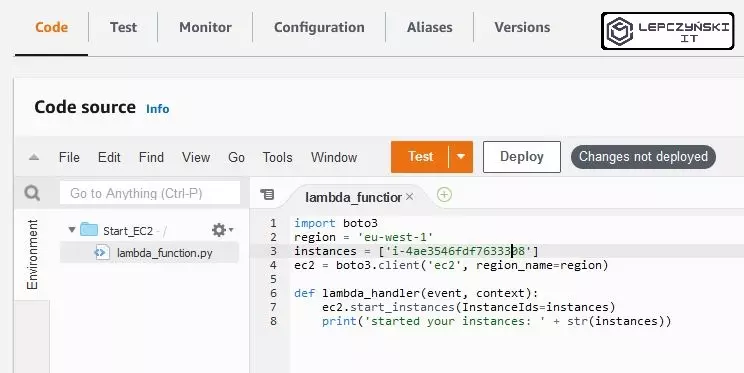
Remember !! If your instance is in a region other than eu-west-1 then correct that as well.
import boto3
region = 'eu-west-1'
instances = ['YOUR_INSTANCE_ID']
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2', region_name=region)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ec2.start_instances(InstanceIds=instances)
print('started your instances: ' + str(instances))Click Deploy when you are done.
Lambda – add trigger
Now you can click Add trigger and schedule your function to run automatically.
Select EventBridge (CloudWatch Evenst) from the list and create a new rule. Provide a name for the function, a description, and specify when you want to run it automatically. I set the start from Monday to Friday at 7:00. When you deal with it, click Add.
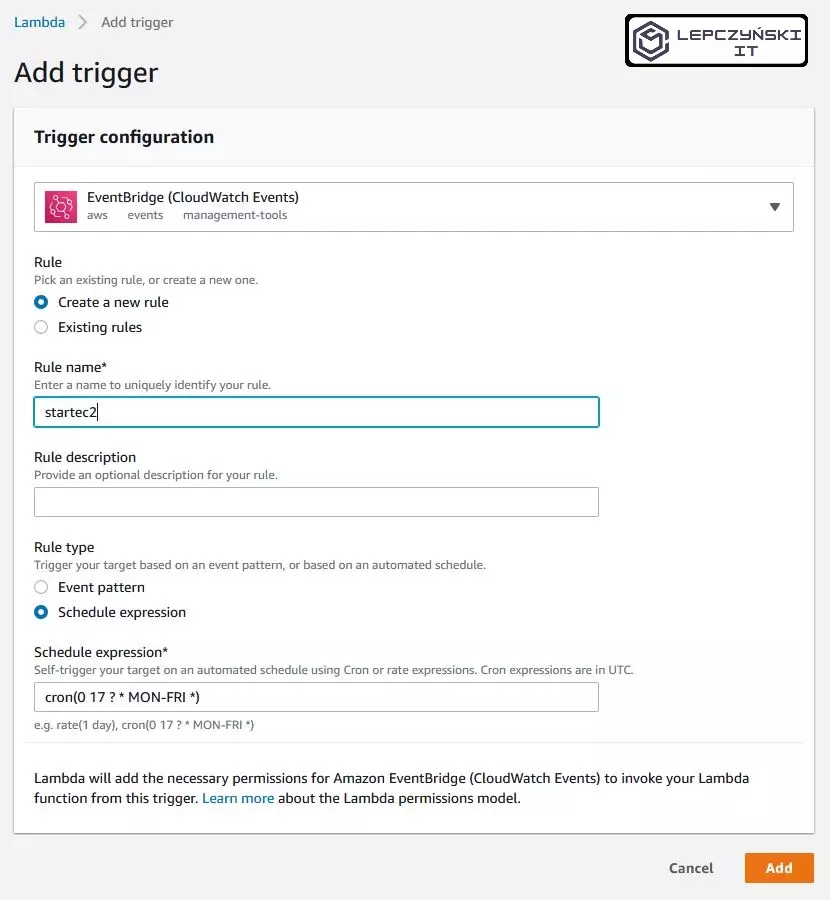
Everything is ready. If you open CloudWatch you will see that your new rule has been added.
Remember !! include time zone. I forgot and I entered the time in GMT, so I should subtract 2 hours to be in line with the CET and the machines started at 7:00 am according to the time in Central Europe🙂. Remember to pay attention to what time zone you need.
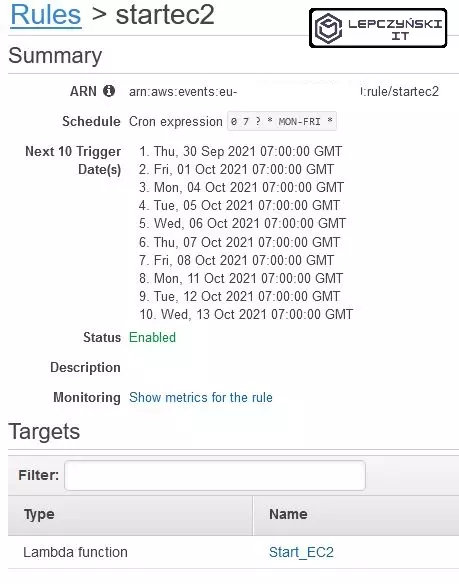
In Cloud Watch, you can also track metrics for the correct execution of a function and add some action if necessary.
Summary
As you can see, the EC2 machines can be started in many different ways. Above I have listed those that I find useful and it is good for you to remember about them. The automatic start of the EC2 machines is just the beginning. Instead, you can issue whatever commands you want and create truly advanced automation. The only limitation here is your imagination 😉. Remember about the appropriate permissions.
In the AWS category you will find all my articles about this cloud. I encourage you to read.
Hi, we need to extend the operating hours for server-test to 24 hours a day during week days (24/5).
The reason is that we will have people from US, Sweden and India working with this server.
The extended operating hours shall be in effect until May 31 2022.
It’s not a problem. Just change the settings in the cron / crontab schedule, e.g. stop the machine on Friday after work and start it on Monday before work.
Comments are closed.